The Evolution of Networks –In today’s digital age, networks play a crucial role in nearly every aspect of our lives. From communication and business to entertainment and education, the way we connect has transformed dramatically over the years. This article explores the evolution of networks, their significance in modern society, and the latest innovations shaping the future of connectivity.
Table of Contents
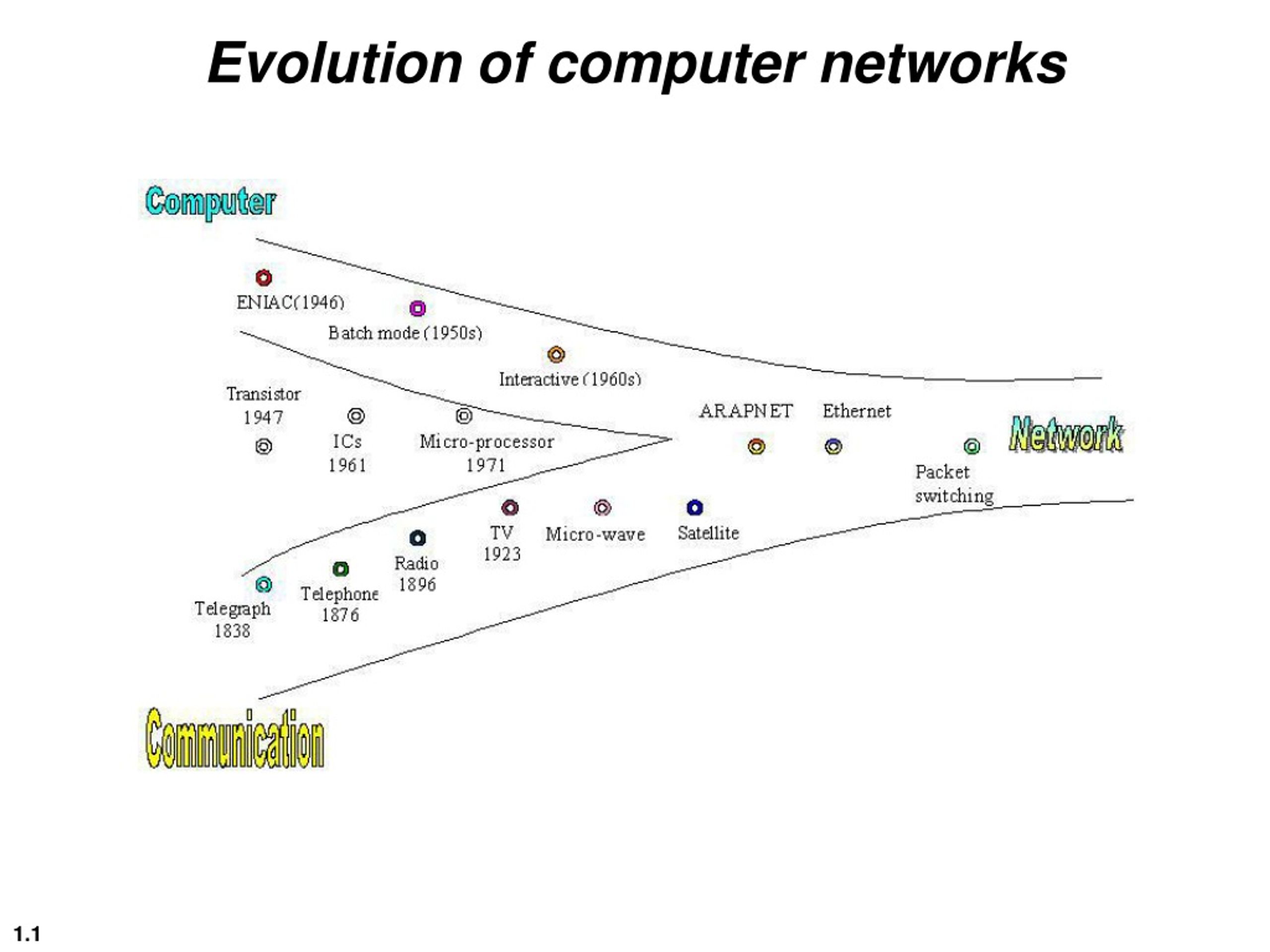
1. The Evolution of Networks: A Journey from Inception to Global Connectivity
Introduction
The modern world thrives on digital connectivity. From instant messaging to seamless video conferencing, networking technology underpins nearly every aspect of our daily lives. But have you ever wondered how it all started? The early days of networking laid the foundation for the global communication systems we rely on today. Understanding this history not only enriches our appreciation of modern innovations but also highlights the transformative impact of networking on society.
The Birth of Computer Networking
Networking, in its simplest form, is the interconnection of computers to share resources and information. The idea of networking began in the 1950s and 1960s, when early computer scientists and engineers sought ways to link computers together for greater efficiency.
ARPANET: The Foundation of the Internet
The most pivotal moment in networking history was the creation of the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) in the late 1960s. Funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, ARPANET was the first packet-switching network that allowed multiple computers to communicate over long distances. The first successful message was sent on October 29, 1969, between a computer at UCLA and another at Stanford University. Though the system crashed after just two letters (“LO” from “LOGIN”), this marked the beginning of a revolutionary era.
The Development of Networking Protocols
For computers to communicate effectively, standardized rules—called protocols—were necessary. Several major developments in networking protocols took place in the early years, shaping the way data is transmitted today.
The Emergence of TCP/IP
The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) was developed in the 1970s by Vinton Cerf and Robert Kahn. These protocols became the backbone of modern networking, allowing computers across different networks to communicate reliably. By 1983, ARPANET officially transitioned to TCP/IP, forming the early structure of what would later become the Internet.
The Transition from Closed Networks to Open Communication
In the early years, networking was primarily limited to military and research institutions. However, the demand for broader accessibility led to significant innovations that allowed businesses, universities, and eventually the public to connect.
Ethernet: The Local Networking Revolution
Developed by Robert Metcalfe in the 1970s, Ethernet provided a way for computers within a single location to connect through wired networks. This technology paved the way for the development of Local Area Networks (LANs), which became essential in corporate and educational environments.
The Rise of Bulletin Board Systems (BBS)
Before the World Wide Web, Bulletin Board Systems (BBS) served as an early form of online communities. Users could dial in using modems, exchange messages, and download files. Though primitive compared to modern internet forums, BBS represented a crucial step in making digital communication accessible to the public.
The Birth of the Internet and Its Impact on Society
The 1990s saw the transition from research-focused networking to a public and commercial internet. The invention of the World Wide Web (WWW) by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 revolutionized the way people accessed and shared information. This period also saw the rise of ISPs (Internet Service Providers), allowing households to connect via dial-up connections.
Networking and Its Influence on Modern Life
Today, networking plays a crucial role in virtually every industry:
- Business and Commerce: E-commerce giants like Amazon and digital payment systems depend on fast and secure networking technologies.
- Education: Online learning platforms and digital libraries make knowledge accessible worldwide.
- Social Interaction: Social media networks have transformed the way we communicate and form relationships.
- Healthcare: Telemedicine and remote patient monitoring rely on strong networking infrastructures.
The Future of Networking
Networking continues to evolve rapidly, with emerging technologies such as 5G, quantum networking, and decentralized web reshaping the digital landscape. As artificial intelligence and automation become more integrated into networking infrastructure, we can expect even greater efficiency and security.
2. The Rise of the Internet: How It Transformed Our World
Introduction
The internet has reshaped the way we live, work, and communicate. From its humble beginnings as a government research project to becoming a global necessity, the internet has revolutionized modern society. Today, it serves as the backbone of countless industries, enabling real-time communication, e-commerce, entertainment, and education. But how did we get here, and what does the future hold for this ever-evolving technology?
The Origins of the Internet
The origins of the internet date back to the 1960s when the U.S. Department of Defense initiated ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network). This early network was designed for military communication and research collaboration among universities. By the 1980s, the foundation for the modern internet was laid with the development of the TCP/IP protocol, allowing different networks to communicate seamlessly.
The invention of the World Wide Web by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 marked a significant turning point. It introduced web pages, hyperlinks, and browsers, making the internet more accessible to the general public. By the mid-1990s, internet service providers (ISPs) started offering dial-up connections, leading to widespread adoption.
The Internet’s Impact on Society
1. Communication Revolution
One of the most profound effects of the internet is the transformation of communication. Emails, instant messaging, and social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have replaced traditional methods of communication. Video conferencing tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams have become indispensable, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated remote work and virtual meetings.
2. The E-Commerce Boom
The rise of the internet has dramatically changed consumer behavior. Online shopping platforms such as Amazon, eBay, and Alibaba have revolutionized retail, offering convenience, variety, and competitive pricing. Businesses have shifted towards digital marketing strategies, utilizing SEO, PPC advertising, and influencer marketing to attract customers globally.
3. Education and E-Learning
The internet has democratized education. Online learning platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy provide access to quality education from anywhere in the world. Universities now offer online degrees, allowing students to learn at their own pace. The shift to e-learning became even more apparent during the pandemic, highlighting the internet’s role in bridging educational gaps.
4. The Digital Economy and Remote Work
Freelancing and remote work have flourished due to the internet. Platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and LinkedIn have enabled professionals to work from anywhere, reducing the need for physical offices. Cloud computing services such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and Microsoft Azure facilitate seamless collaboration, making remote work more efficient than ever before.
5. Entertainment and Media Evolution
The entertainment industry has been transformed by streaming services like Netflix, YouTube, and Spotify. Traditional television and radio have been supplemented (or even replaced) by on-demand content. Social media has also become a primary news source, although this has raised concerns about misinformation and fake news.
6. The Rise of Social Media and Its Influence
Social media has not only changed personal interactions but has also impacted politics, marketing, and activism. Movements such as #MeToo and Black Lives Matter gained momentum through online platforms. However, issues like cyberbullying, data privacy concerns, and algorithm-driven echo chambers have also emerged as significant challenges.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its numerous benefits, the internet presents several challenges:
- Cybersecurity Threats: Hacking, phishing, and data breaches put individuals and businesses at risk.
- Digital Divide: Not everyone has equal access to the internet, creating disparities in opportunities and information access.
- Privacy Issues: Data collection and surveillance by tech companies have raised ethical concerns.
- Misinformation and Fake News: The spread of misleading content has influenced public opinion and elections.
The Future of the Internet
The internet is constantly evolving. Emerging technologies such as 5G, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the metaverse are set to redefine our online experiences. The concept of Web3—a decentralized internet built on blockchain technology—aims to give users more control over their data and online interactions.
With innovations like the Internet of Things (IoT) connecting everyday devices, smart cities and automation will become more prevalent. However, with these advancements come concerns about data security, AI ethics, and the environmental impact of digital infrastructures.
3. The Mobile Revolution: Transforming Lives in the Digital Era
Introduction
The world has changed dramatically in the past two decades, and at the heart of this transformation lies the mobile revolution. The evolution of mobile technology has redefined communication, work, entertainment, and even the way societies function. Today, smartphones and mobile devices have become indispensable, influencing various industries and reshaping human interactions. This article explores the latest trends in mobile technology, its relevance to daily life, and the profound impact it has on society.
The Evolution of Mobile Technology
The Early Days: From Analog to Digital
Mobile communication started with basic analog phones that allowed voice calls. The introduction of 2G networks brought SMS messaging, and 3G expanded capabilities with mobile internet access. However, it was the arrival of 4G that truly revolutionized mobile usage, enabling high-speed data transfer, video streaming, and app-driven services.
The 5G Revolution
The most recent leap in mobile technology is 5G, promising ultra-fast connectivity, lower latency, and increased device capacity. This technology is not just about faster internet speeds but also about enabling new possibilities such as smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and enhanced IoT (Internet of Things) applications.
The Impact of Mobile Technology on Society
Communication and Connectivity
Smartphones have made communication more immediate and accessible. With apps like WhatsApp, Zoom, and social media platforms, people can stay connected regardless of geographical boundaries. This has transformed personal relationships and business interactions alike.
The Gig Economy and Remote Work
Mobile technology has facilitated the rise of the gig economy, where freelancers and remote workers can work from anywhere. Platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, and Uber rely on mobile applications to connect service providers with customers, making employment more flexible and accessible.
Mobile Commerce and Digital Payments
E-commerce has surged with the advent of mobile payments. Services like Apple Pay, Google Wallet, and various fintech apps have enabled cashless transactions, reducing the need for physical currency. This has accelerated digital banking and financial inclusion, particularly in developing regions.
Healthcare and Telemedicine
Mobile technology has transformed healthcare through telemedicine, allowing patients to consult doctors remotely. Mobile health (mHealth) apps help individuals monitor their health, track fitness, and even access mental health resources. This is particularly beneficial for those in remote areas with limited healthcare facilities.
Education and E-Learning
The accessibility of education has improved significantly with mobile technology. Online courses, virtual classrooms, and mobile learning platforms provide students with the opportunity to gain knowledge from anywhere. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Duolingo exemplify how mobile learning has revolutionized education.
The Future of Mobile Innovation
Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Devices
AI is enhancing mobile experiences by improving voice assistants (like Siri and Google Assistant), personalizing content recommendations, and optimizing app functionalities. AI-driven automation is also streamlining workflows across industries.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are gaining traction in mobile applications, enhancing gaming, shopping, and even education. Retail brands are using AR to offer virtual try-ons, while VR is revolutionizing remote collaboration and immersive experiences.
Sustainability in Mobile Technology
The mobile industry is shifting towards sustainability by developing eco-friendly devices, using recyclable materials, and reducing electronic waste. Brands like Apple and Samsung are investing in green initiatives, ensuring a more sustainable future for mobile technology.
2. Business and Economy
Networks have become the backbone of modern businesses. From cloud computing to e-commerce, companies rely on robust networking infrastructures to operate efficiently. Remote work, enabled by strong internet connections, has reshaped the workforce landscape.
3. Education and E-Learning
With the rise of online education, students can now access high-quality learning resources from anywhere. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Khan Academy leverage network technology to provide interactive learning experiences.
4. Healthcare and Telemedicine
Telehealth services have gained traction, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic. Doctors can now consult with patients remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving access to medical care.
The Latest Innovations in Networking
1. 5G and Beyond
5G technology promises ultra-fast internet speeds, lower latency, and improved connectivity. As industries adopt 5G, new possibilities emerge, including smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and enhanced virtual reality experiences.
2. Edge Computing
Unlike traditional cloud computing, edge computing processes data closer to its source, reducing latency and improving efficiency. This innovation is critical for real-time applications like IoT and industrial automation.
3. Blockchain and Decentralized Networks
Blockchain technology is disrupting traditional networking by offering secure and transparent data transactions. Decentralized networks eliminate the need for intermediaries, improving security and efficiency.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Network Optimization
AI-driven networking solutions help predict and prevent connectivity issues, enhancing overall performance. Machine learning algorithms analyze data patterns to optimize bandwidth usage and reduce downtime.
The Future of Networks
As technology continues to advance, networks will become even more intelligent and interconnected. The integration of AI, quantum computing, and next-generation wireless technologies will redefine connectivity, making digital experiences more seamless than ever before.
Conclusion
Networks have evolved from simple communication systems to complex infrastructures that power the modern world. As innovations continue to reshape connectivity, businesses and individuals must adapt to these changes to stay ahead in an increasingly digital society. With the rapid development of 5G, AI, and blockchain, the future of networks holds endless possibilities, ensuring a more connected and efficient world for generations to come.